Congrats to Ms. Shi Xiaoyun on ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces publication
文章来源: 发布日期: 2024-11-21
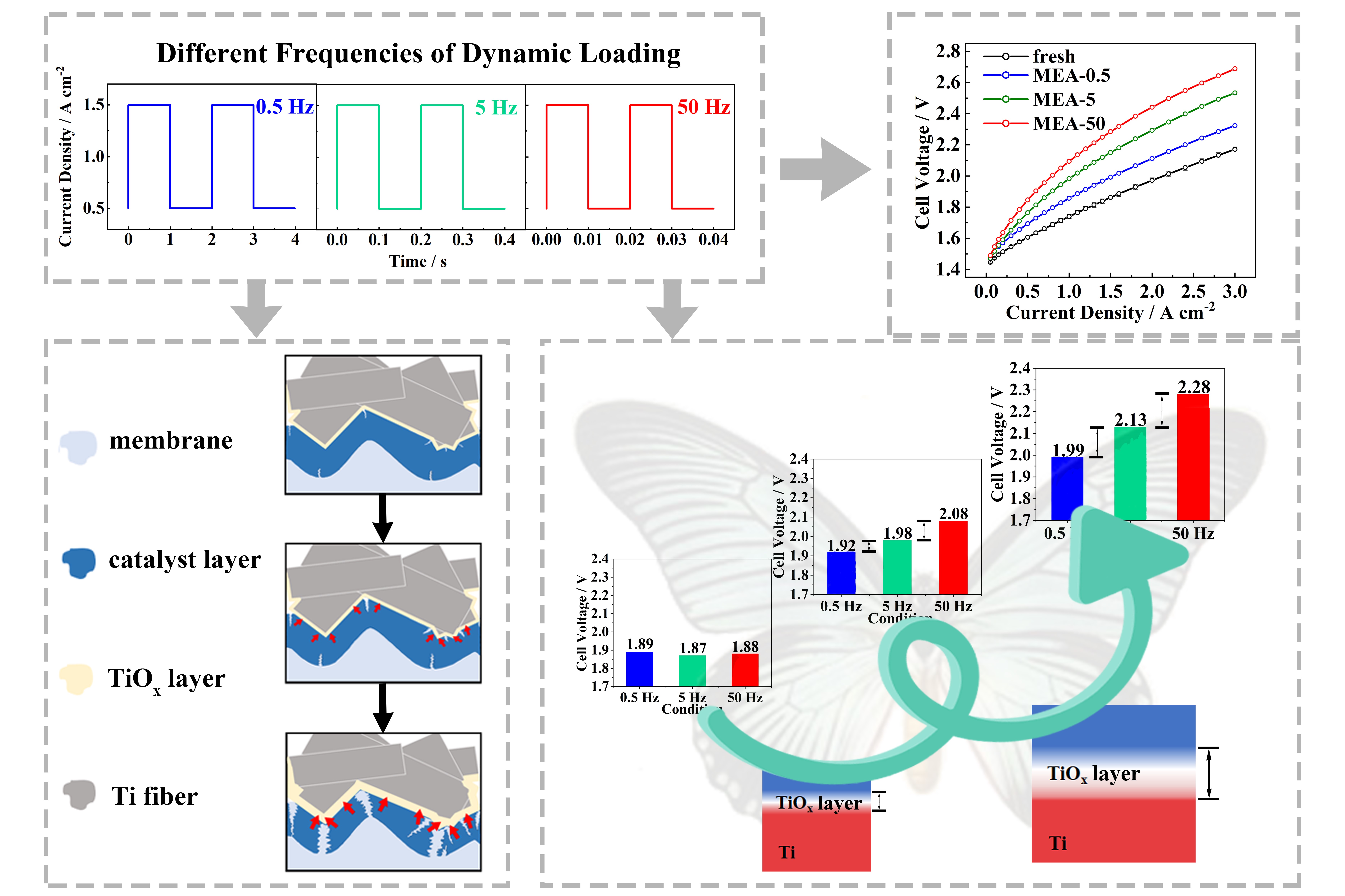
Green hydrogen production via PEM water electrolysis is challenged by fluctuating inputs power when coupled with renewable energy sources. This study investigates the effects of dynamic loading frequencies on membrane electrode assemblies’ (MEAs) performance and durability. We found that higher loading frequencies facilitate the growth of oxide layer of Ti porous transport layer (Ti-PTL) due to increased duration in voltage spike region. These thicker and coarser oxide layers directly induce cracks and delamination in the anodic catalyst layers by spontaneously adsorbing ionomer. These changes negatively impact interface contact quality and anodic electrochemical active area, ultimately reducing the performance of the MEA, with higher frequencies accelerating this degradation. Additionally, applying a Pt coating on PTL effectively mitigates these adverse effects. This work highlights the importance of dynamic loading studies and reveals that effective management of Ti-PTL and catalyst/PTL interface is necessary to achieve long-term operational durability of PEM water electrolysis.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.4c13605